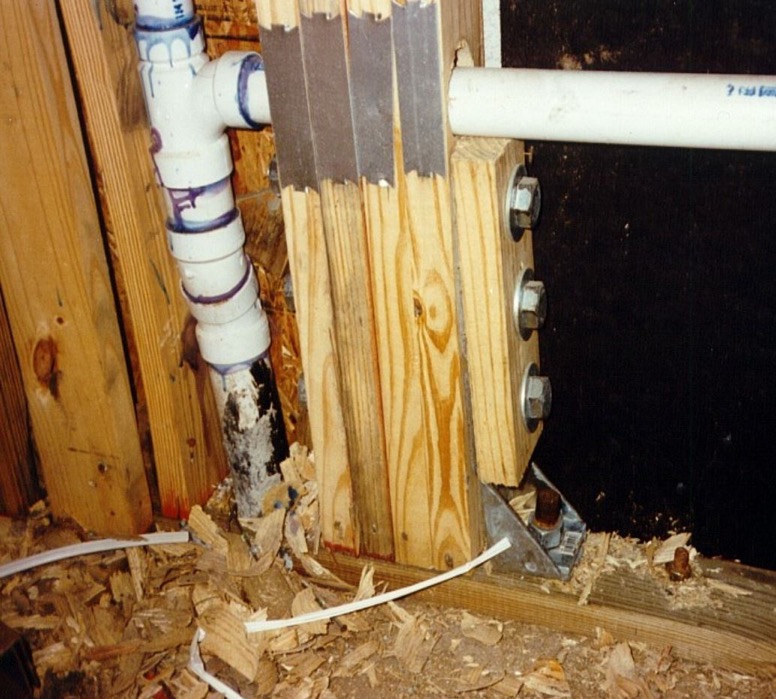
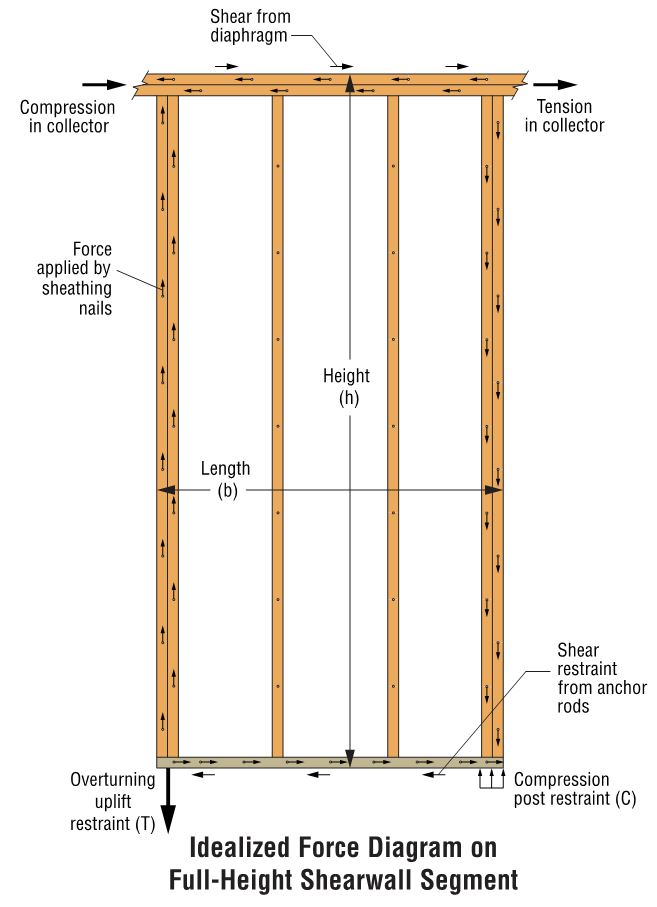
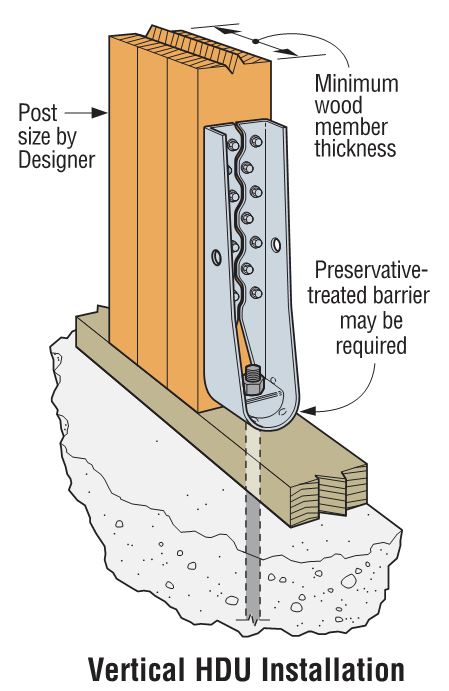
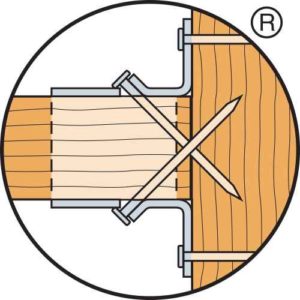
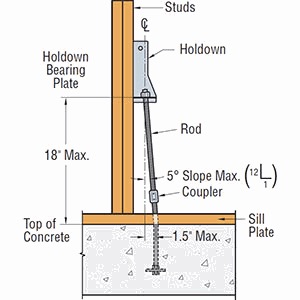
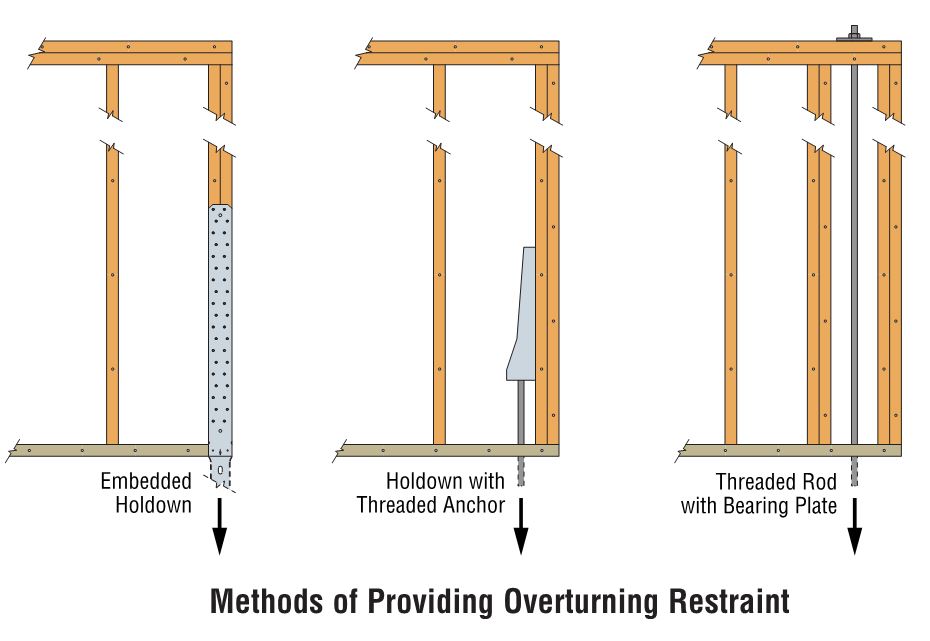
Keith Cullum started off our “How to Select a Connector” series with Hurricane Ties. This week we will discuss how to select holdowns and tension ties, which are key components in a continuous load path. They are used to resist uplift due to shearwall overturning or wind uplift forces in light-frame construction. In panelized roof construction, holdowns are used to anchor concrete or masonry walls to the roof framing.
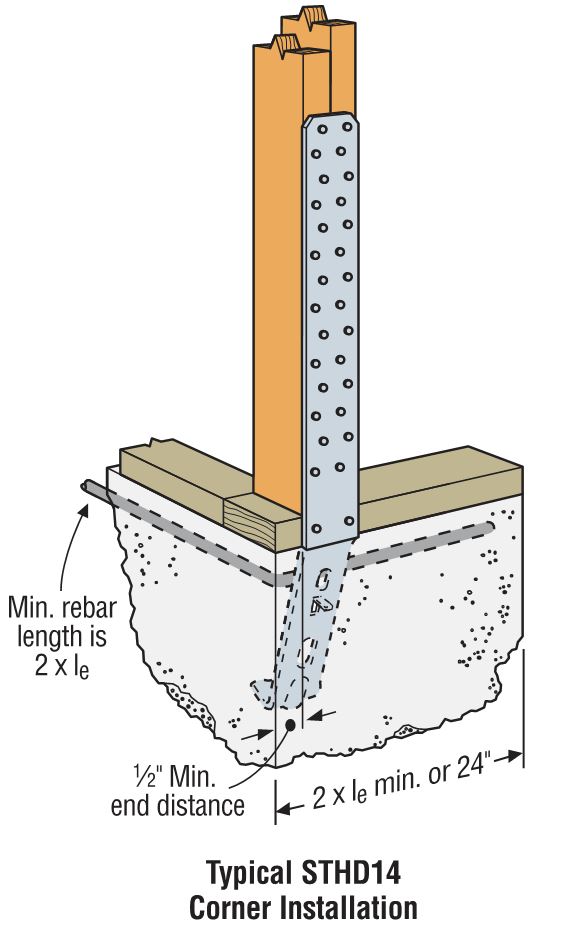
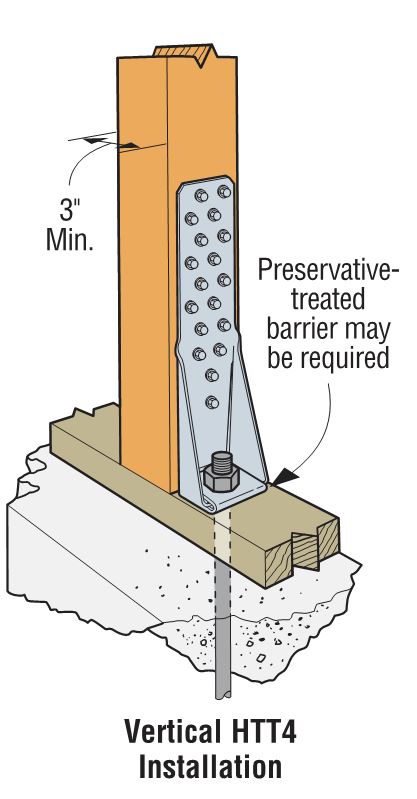
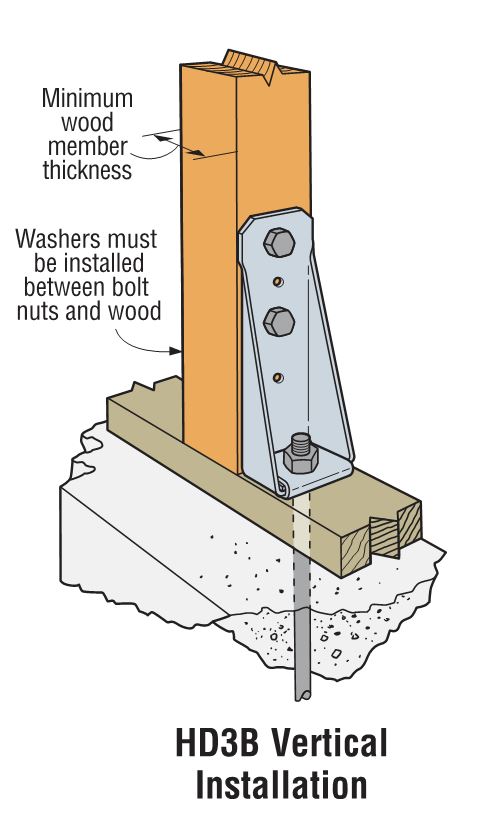
Holdowns can be separated in two basic categories – post-installed and cast-in-place. Cast-in-place holdowns like the STHD holdowns or PA purlin anchors are straps that are installed at the time of concrete placement. They are attached with nails to wood framing or with screws to CFS framing. After the concrete has been placed, post-installed holdowns are attached to anchor bolts at the time of wall framing. The attachment to wood framing depends on the type of holdowns selected, with different models using nails, Simpson Strong-Tie® Strong-Drive® SDS Heavy-Duty Connector screws or bolts.
A third type of overturning restraint is our anchor tiedown system (ATS), which is common in multistory construction with large uplift forces. I discussed the system in this blog post.
 Given the variety of different holdown types, a common question is, how do you choose one?
Given the variety of different holdown types, a common question is, how do you choose one?
For prescriptive designs, such as the IRC portal frame method, the IRC or IBC may require a cast-in-place strap-style holdown. Randy Shackelford did a great write-up on the PFH method in this post.
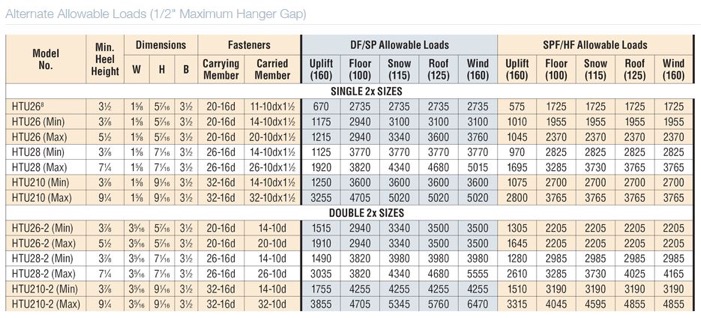
For engineered designs, a review of the design loads may eliminate some options and help narrow down the selection.
| Holdown Type | Maximum Load (lb.) |
| Cast-in-Place | 5,300 |
| Nailed | 5,090 |
| SDS Screws | 14,445 |
| Bolted | 19,070 |
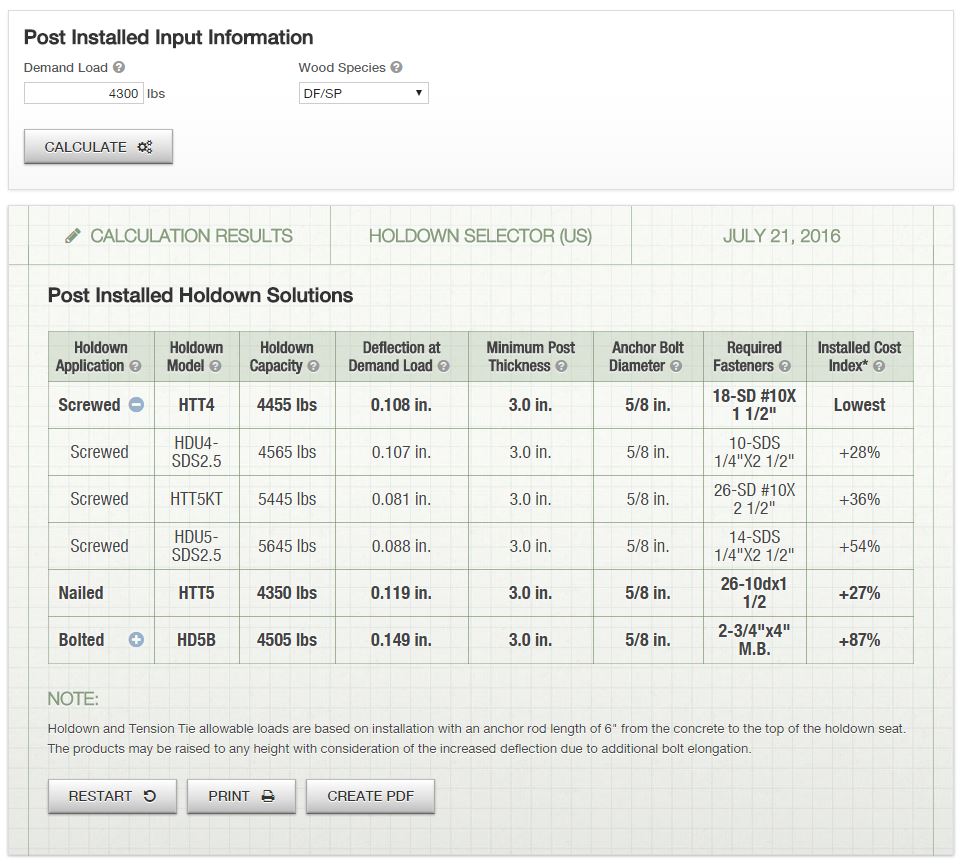
I like flipping through catalog pages, but our Holdown Selector App is another great tool for selecting a holdown to meet your demand loads. Select cast-in-place or post-installed, enter your demand load and wood species, and the application will list the holdown solutions that work for your application.
The application lists screwed, nailed and bolted solutions that meet the demand load in order of lowest installed cost, allowing the user to select the least expensive option.
Adjustability should be considered when choosing between a cast-in-place and a post-installed holdown. Embedded strap holdowns are economical uplift solutions, but they must be located accurately to align with the wood framing. If the anchor bolt is located incorrectly for a post-installed holdown, raising the holdown up the post can solve many problems. And anchors can be epoxied in place for missing anchor bolts.
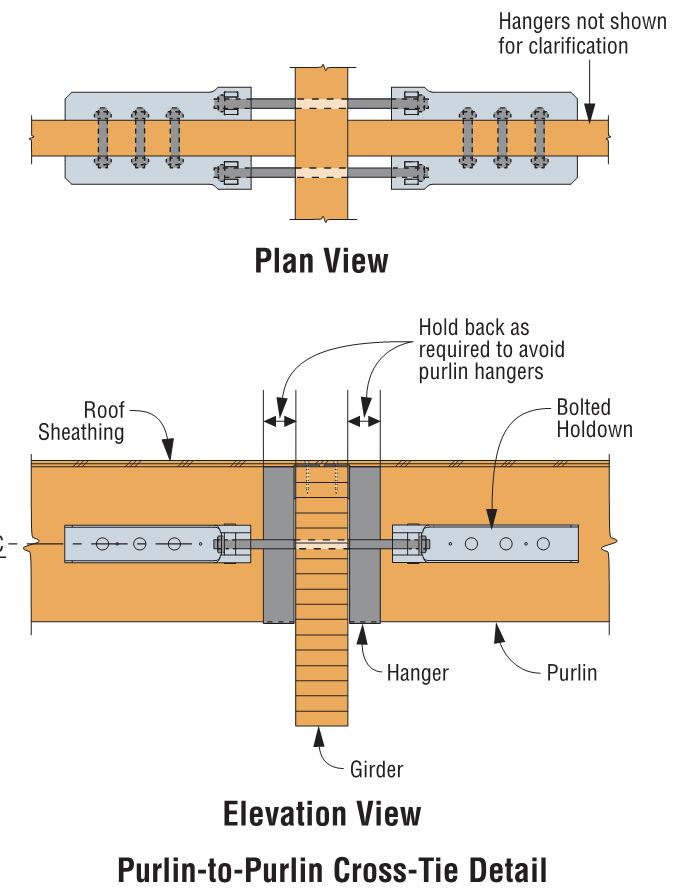
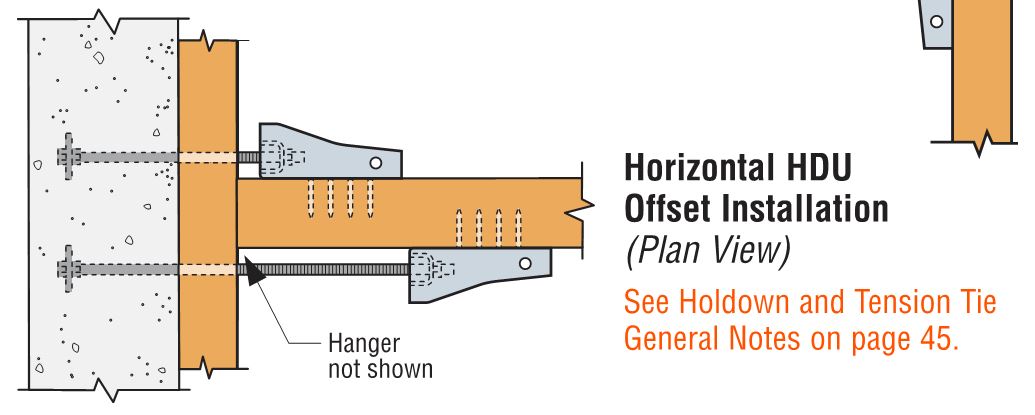
 We are often asked if you can double the load if you install holdowns on both sides of the post or beam. The answer is yes, and this is addressed in our holdown general notes.
We are often asked if you can double the load if you install holdowns on both sides of the post or beam. The answer is yes, and this is addressed in our holdown general notes.
Nailed or screwed holdowns need to be installed such that the fasteners do not interfere with each other. Bolted holdowns do not need to be offset for double-sided applications. Regardless of fastener type, the capacity of the anchorage and the post or beam must be evaluated for the design load.
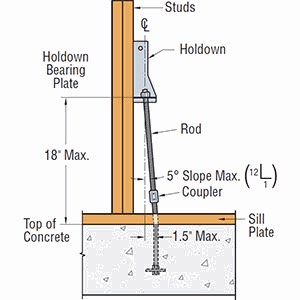
Once you have selected a holdown for your design, it is critical to select the correct anchor for the demand loads. Luckily, I wrote a blog about Holdown Anchorage Solutions last year. What connector would you like to see covered next in our series? Let us know in the comments below.