Mass timber buildings use cross-laminated timber (CLT) or mass plywood panels to create horizontal diaphragms to transfer wind and seismic forces into the vertical elements of the lateral-force-resisting system. Spline connections resist shear forces at the panel joints, which I discussed in this blog post. I wanted to discuss several options for tension straps used for chord splices and collector forces. This blog will not discuss methods for calculating design forces. Instead, I am going to focus on several strap products and how we developed their allowable loads.
Straight straps are one of the few connector products where allowable loads are based on calculations, not testing. For joist hangers, hurricane ties or holdowns, there are all sorts of eccentricity that create shear, prying and withdrawal forces on the fasteners and difficult-to-predict load distribution in the connector. Straight straps don’t have any of that, so we can calculate the steel tension capacity and the fastener capacity per code. However, Simpson Strong-Tie has tested many of our straps because we really love testing. We also receive questions sometimes about deflection or whether or not you can install a given strap over plywood (you can, as long as you use nails 2½” or longer).
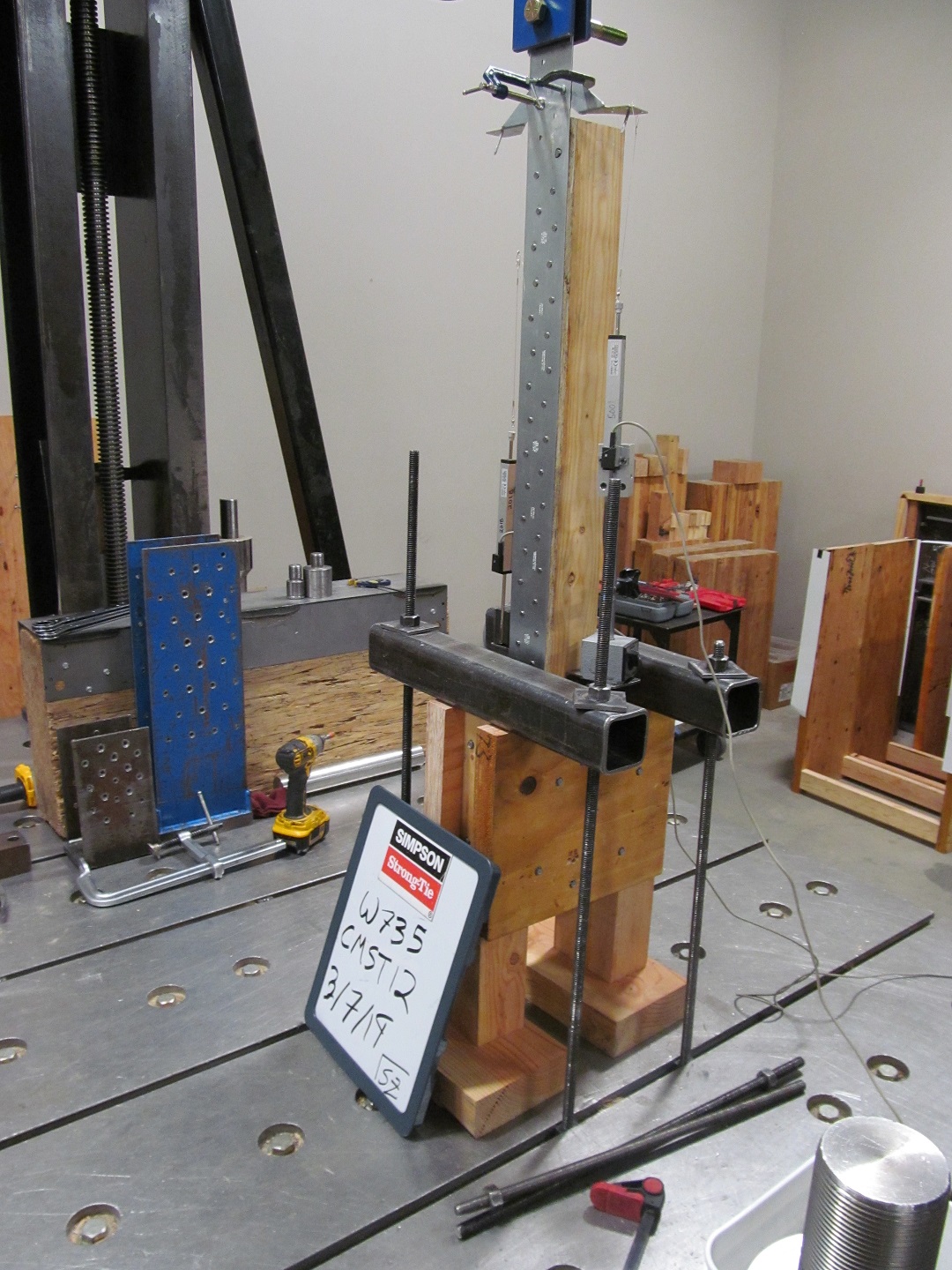



Nailed tension straps have allowable loads ranging from 605 pounds (HRS6) to 9,215 pounds (CMST12). In mass timber diaphragms, forces often exceed these capacities. We have seen engineers specify multiple straps or custom steel plates to achieve higher loads at splice locations. To help reduce cost and speed up installation, Simpson Strong-Tie developed the MDCST – Medium Duty Diaphragm Chord Strap Tie. The MDCST is a 14-gauge strap that uses Strong-Drive® SDS Heavy-Duty Connector screws.
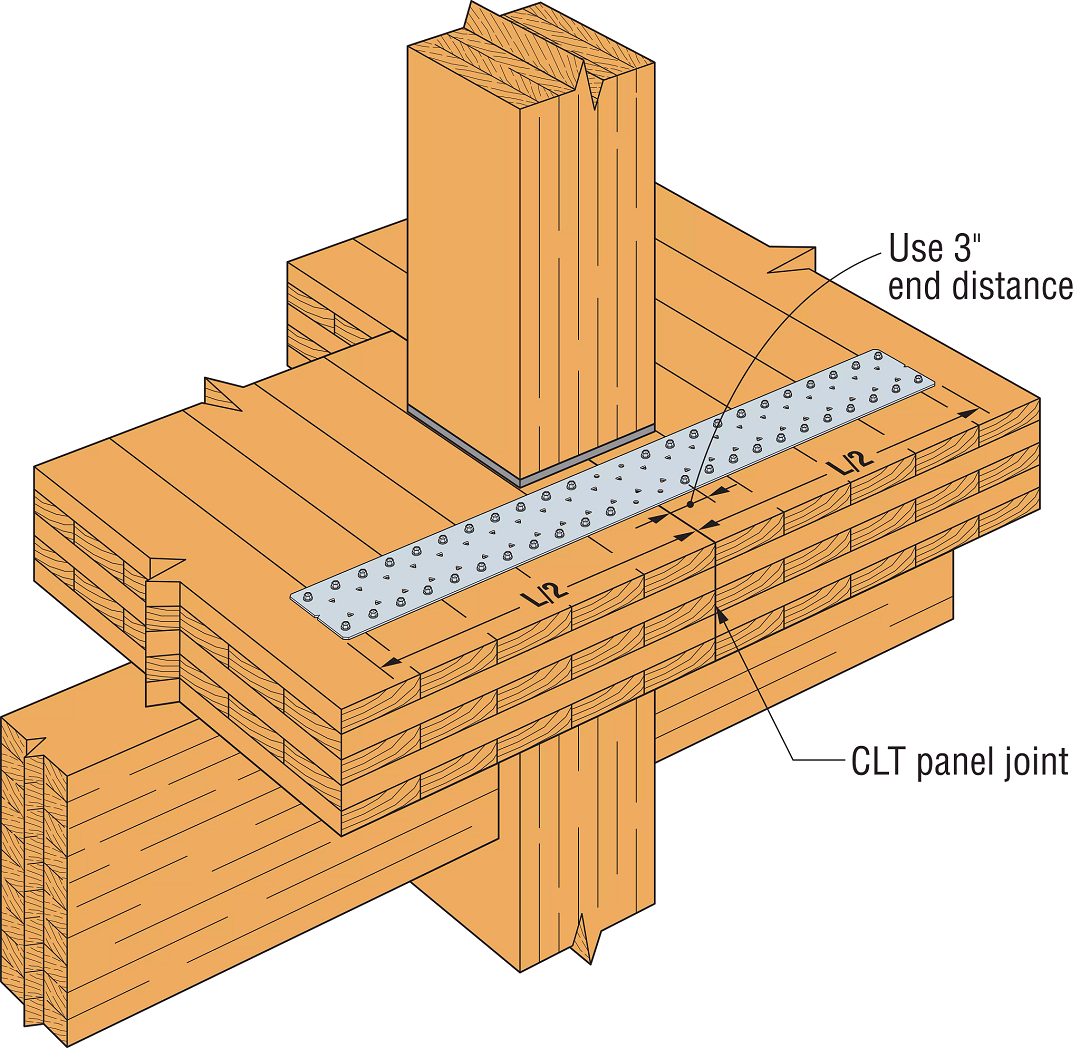
The MDCST48 has an allowable load of 11,905 pounds and can be overlapped to achieve double the load where space is limited. North American CLT manufacturers do not glue the edges of the CLT plies together. To evaluate whether these unglued edges would affect the capacity of the SDS screws, we tested the MDCST48 on CLT. Calculations predicted the strap tensile capacity would govern the allowable load and our assembly tests validated the calculation model.
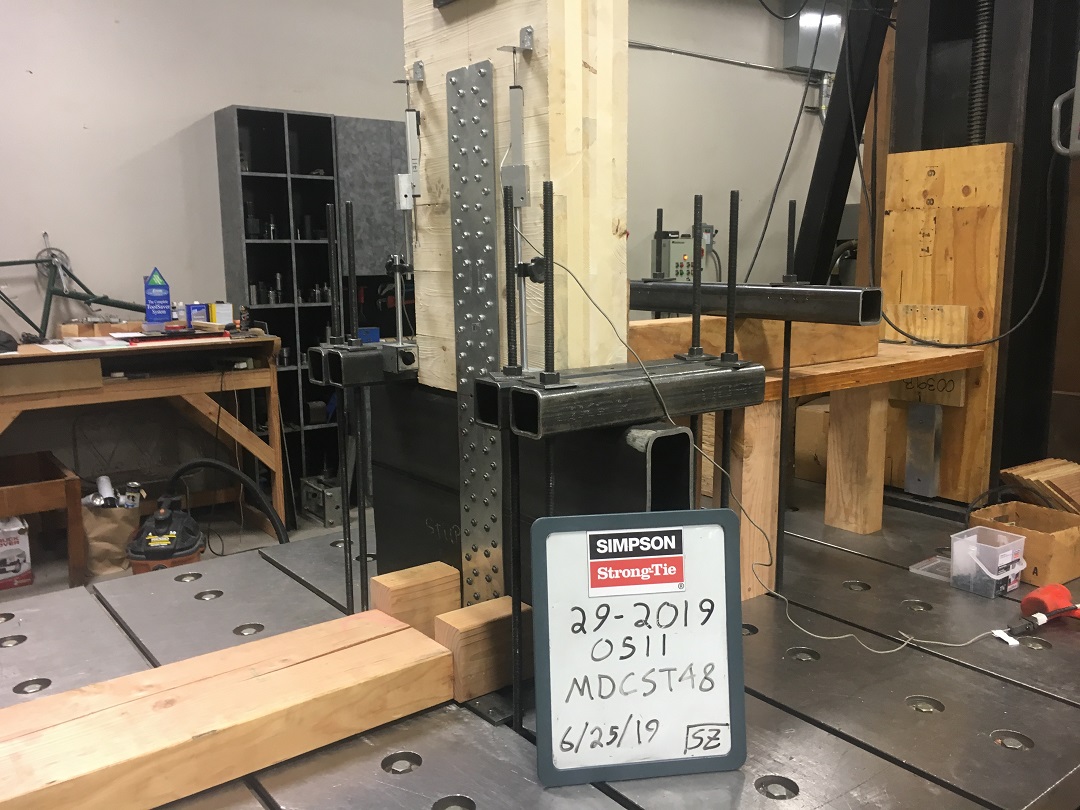


After releasing the MDCST, we wanted to develop a high-capacity tension strap using fewer fasteners. We combined two products to do this. The Strong-Drive SDCF Timber-CF Screw is a fully threaded screw designed for mass timber. The threads on the SDCF maximize withdrawal resistance for their original intended uses as beam reinforcement, bearing reinforcement, and splitting reinforcement. The MTW45-8 Mass Timber Angled Washer allows SDCF installation through a steel side plate at a 45-degree angle. Traditional fasteners transfer shear load through shank bearing on the wood. Installing the fastener at an angle allows us to transfer shear loads through the fastener in tension. The high-withdrawal capacity of the SDCF creates a strong, stiff connection allowing high loads with fewer fasteners.
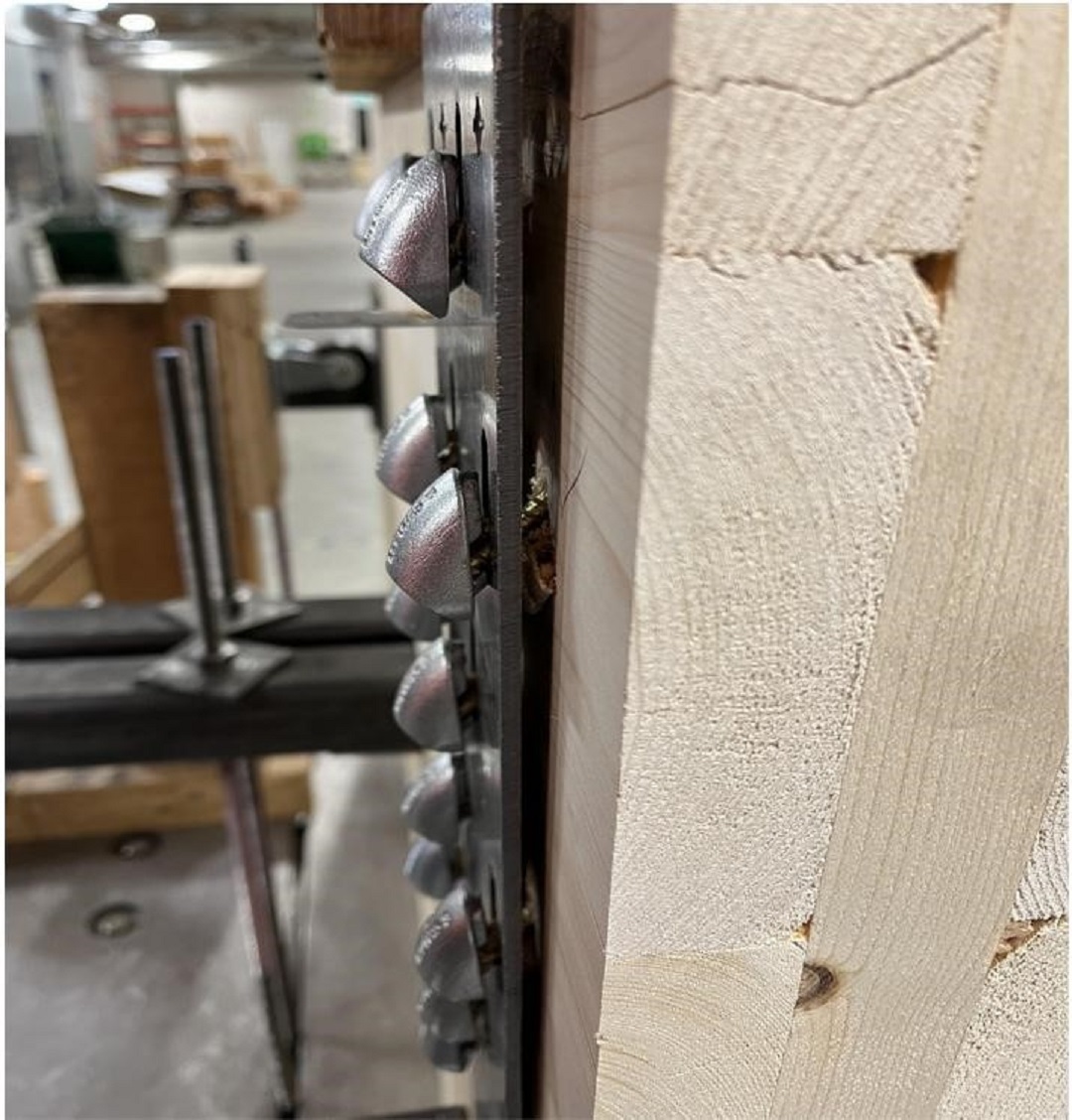


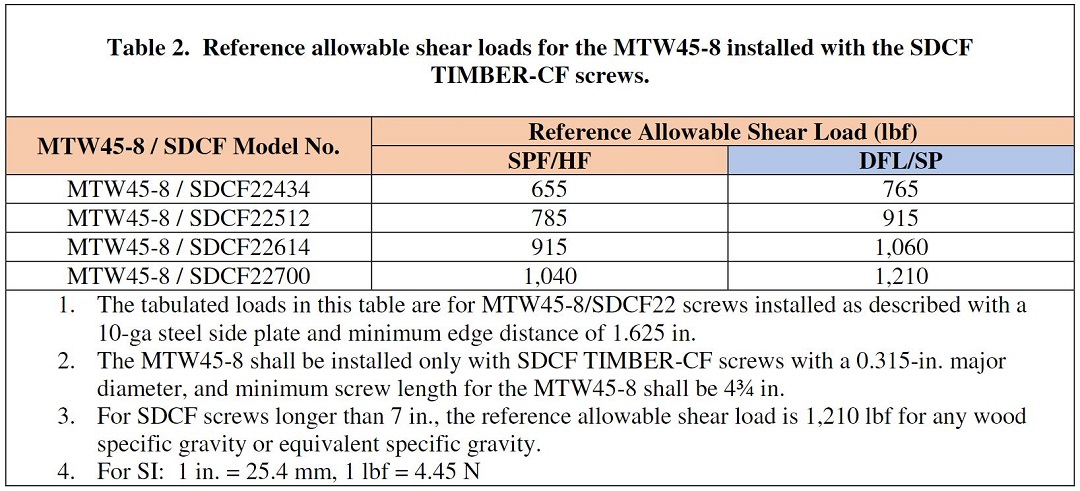
The reference allowable shear loads for the MTW45-8 installation with SDCF Timber-CF screws are based on our testing of individual or small groups of fasteners. I discussed fastener testing in So, What’s Behind a Screw’s Allowable Load? We also performed larger group testing to determine appropriate group action reduction factors. We’ve summarized the allowable loads, stiffness behavior, and design procedure in an engineering letter, L-MTW45SDCF24. Engineers can use the procedure to design custom connections for plate thickness between ⅛” and ½”.

While you could design a strap, picking one out of a load table is easier. The MTWS Mass Timber Washer Strap is a high-capacity strap designed for use with inclined SDCF Timber-CF screws in MTW45-8 washers. It comes in two widths and has allowable loads for three-ply and five-ply (or thicker) mass timber panels.



