When you’re building a deck, it’s important to know the types of fasteners you need to use with the various materials that are available. On this week’s post we explore some deck fastener applications as well as offer suggestions on how to avoid a few common problems. We will address two generic types of deck boards fastened to wood framing: preservative-treated wood and composite decking.
Preservative-Treated Wood Decking
With preservative treated wood, it pays to know the board treatment. Wood is treated with a water-borne treatment chemical (typically micronized copper azole these days) and then it is either sent out wet or it is kiln dried. Wet-treated wood can have a moisture content (MC) greater than 30%. Wood that is subsequently kiln dried to remove excess moisture after the treatment process is labeled Kiln-Dried After Treatment (KDAT) and has a MC of about 15%. Wood deck boards with preservative treatments will be labeled as such regardless of their moisture condition.
The moisture condition of the deck boards determines how best to fasten and space your deck boards. Wet wood will shrink in width and thickness after installation. As a result, you should install these boards butted tight so that gaps will emerge after they dry in place. On the other hand, KDAT wood or wood that is dry should be installed with 1/8” gaps between boards so there is a slight gap after the boards get wet and swell due to rain, ice and snow. Some manufacturers suggest using an 8d common nail for spacing when installing KDAT decking, as seen in the figure below.
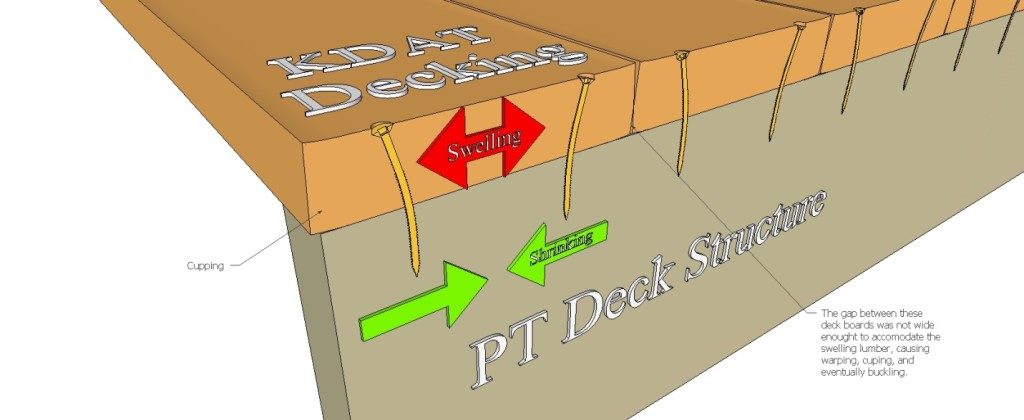
Shrinking and swelling of any installed deck board can cause the deck fastener to bend back and forth with the MC cycling. This causes many deck fasteners to break because of the fatigue loading, which can be exacerbated by the brittle steel used in most deck screws.
To combat this problem, Simpson Strong-Tie developed the DSV Wood screw. This screw is specifically designed with increased ductility to handle the bending induced by deck board movement. It is available in a variety of lengths with threads optimized to prevent jacking between the deck board and the framing, ensuring a snug long-lasting connection.
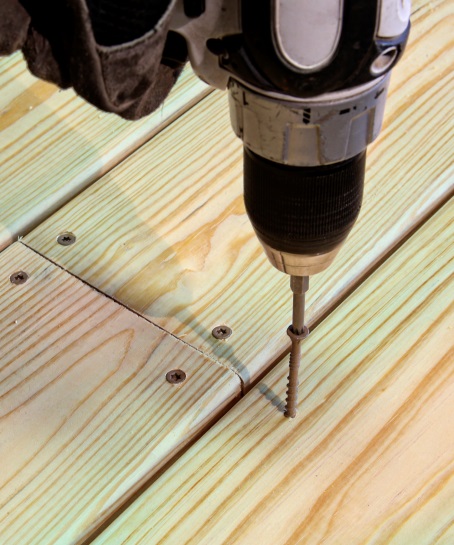

Composite deck boards are made from a mixture of wood fiber and plastic or are entirely “plastic.” Wood plastic composites and plastic materials exhibit thermal expansion, so they expand and contract in thickness, width and length as a function of temperature and solar heating. Consequently, they typically require a special screw designed for composite decking. Screws for this application will often utilize a two-thread design. The lower thread drives the screw into the framing while the upper thread pulls the loosened composite material back into the hole and holds the deck board tight to the joist. Composite screws also have a cap-style head that covers any residual material left around the screw body and leaves a clean finish. Ductility is important to these screws too.
Given the wide variety of composite deck producers, we designed a screw that works well with all of them. The DCU screw works in all types of composite decking fastened to wood framing.
A note about cellular PVC deck boards: the manufacturers’ recommendation of stainless-steel screws restricts the use of many deck board fasteners. Be sure to read and follow the decking material fastener requirements. Simpson Strong-Tie has a broad offering of painted stainless-steel deck screws available to match PVC deck boards. Find the proper match for your board here.
For other deck fastener applications, including decking fastened to steel framing, and information about other deck fasteners available, see our website product page.
Are there other applications that you want to know about that we didn’t share here? Let us know in the comments below. As always, call us in the Engineering Department if you have questions.

