With the growing danger of natural disasters, the race is on to expand access to programs that safeguard lives from the human-made danger of poorly built housing. With the common mission of building safer, stronger structures, Build Change and Simpson Strong-Tie announced the renewal of the Simpson Strong-Tie® Fellowship for Engineering Excellence program.
Continue Reading
Tag: seismic retrofit
Simpson Strong-Tie Build Change Fellow Visits Manila
This week’s post was written by James P. Mwangi, Ph.D., P.E., S.E. — our first annual Simpson Strong-Tie Engineering Excellence Fellow with Build Change. As part of his fellowship he’s been submitting reports about his work supporting the Build Change initiative. This is the last in a series of four.
Continue Reading
5 Steps to a Successful Soft-Story Retrofit
Last year, I gave a presentation at the annual National Council of Structural Engineers Associations (NCSEA) Summit in Orlando, Florida, titled “Becoming a Trusted Advisor: Communication and Selling Skills for Structural Engineers.” As this was a summit for the leaders of the structural engineers associations from across the country, I wasn’t sure how many people would find it valuable to spend their time learning about a very nontechnical topic. To my surprise and delight, the seminar ended up being standing-room only, and I was able to field some great questions from the audience about how they could improve their selling and communication skills. In the many conversations I had with the conference attendees after my presentation, the common theme was that engineers felt they needed more soft-skills training in order to better serve their clients. The problem, however, was finding the time to do so when faced with the daily grind of design work.

When I started my first job as a design engineer at a structural engineering consulting firm straight out of school, I was very focused on improving and expanding my technical expertise. Whenever possible, I would attend building-code seminars, design reviews and new product solution presentations, all in an effort to learn more about structural engineering. What I found as I progressed through my career, however, was that no matter how much I learned or how hardworking I was, it didn’t really matter if I couldn’t successfully convey my knowledge or ideas to the person who really mattered most: the client.

How can an engineer be most effective in explaining a proposed action or solution to a client? You have to be able to effectively sell your idea by understanding the needs of your client as well as any reasons for hesitation. The importance of effective communication and persuasion is probably intuitive to anyone who’s been on the sales side of the business, but not something that occurs naturally to data-driven folks like engineers. As a result of recent legislation in California, however, structural engineers are starting to be inundated with questions from a group of folks who have suddenly found themselves responsible for seismically upgrading their properties: apartment building owners in San Francisco and Los Angeles.
Imagine for a moment that you are a building owner who has received a soft-story retrofit notice under the City of Los Angeles’ Ordinance 183893; you have zero knowledge of structural engineering or what this term “soft-story” even means. Who will be your trusted advisor to help you sort it out? The City of Los Angeles Department of Building and Safety (LADBS) has put together a helpful mandatory ordinance website that explains the programs and also offers an FAQ for building owners that lets them know the first step in the process: hire an engineer or architect licensed in the state of California to evaluate the building.

I’ve had the opportunity to be the first point of contact for a building owner after they received a mandatory notice, because it turns out some relatives own an apartment building with soft-story tuck-under parking. Panicked by the notice, they called me looking to understand why they were being forced to retrofit a building that “never had any problems in the past.” They were worried they would lose rent money due to tenants needing to relocate, worried about how to meet the requirements of the ordinance and, most importantly, worried about how much it was going to cost them. What they really wanted was a simple, straightforward answer to their questions, and I did my best to explain the necessity behind retrofitting these vulnerable buildings and give an estimated time frame and cost that I had learned from attending the first Los Angeles Retrofit Resource Fair in April 2016. With close to 18,000 buildings in the cities of San Francisco and Los Angeles alone that have been classified as “soft-story,” this equates to quite a number of building owners who will have similar questions and be searching for answers.
To help provide an additional resource, Simpson Strong-Tie will be hosting a webinar for building owners in the Los Angeles area who have received a mandatory soft-story retrofit notice. Jeff Ellis and I will be covering “5 Steps to a Successful Retrofit” and helping to set a clear project path for building owners. The five steps that Simpson Strong-Tie will be recommending are:
- Understanding the Seismic Retrofit Mandate
- Partnering with Design Professionals
- Submitting Building Plans with the Right Retrofit Product Solutions
- Communicating with Your Building Tenants
- Completing Your Soft-Story Retrofit
We encourage you to invite any clients or potential clients to attend this informative webinar, which will lay the foundation for great communication between the two of you. As part of the webinar, we will be asking the building owners for their comments, questions and feedback so we can better understand what information they need to make informed decisions, and we will be sure to share these with the structural engineering community in a future post. By working together to support better communication and understanding among all stakeholders in retrofit projects, we will be well on our way to creating stronger and more resilient communities!
For additional information or articles of interest, there are several resources available:
- Register for the “5 Steps to a Successful Retrofit” webinar on April 26
- Register to attend the 2nd Los Angeles Seismic Retrofit Resource Fair on April 17 (and stop by the Simpson Strong-Tie booth!)
- Find a structural engineer through the Structural Engineers Association of Southern California (SEAOSC)
- Resilience by Design: City of Los Angeles Lays Out A Seismic Safety Plan
- City of San Francisco Implements Soft-Story Retrofit Ordinance
- Soft-Story Retrofits Using the New Simpson Strong-Tie Retrofit Design Guide
- Visit the Simpson Strong-TieSoft-Story Retrofit Center
- The Los Angeles Times Soft-Story Map
Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drill 2016
The Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drill is an annual opportunity for people in homes, schools and organizations to practice what to do during earthquakes and improve their preparedness. In a post I wrote last October about the Great ShakeOut, I reminisced about the first earthquake I had to stop, drop and cover for – the Livermore earthquake in January, 1980. This year got me thinking about how our evacuation drills work.
At Simpson Strong-Tie, we use the annual Great ShakeOut drill to practice our building evacuation procedures. Evacuation drills are simple in concept – alarms go off and you exit the building. We have volunteer safety wardens in different departments who confirm that everyone actually leaves their offices. There are always a few people who want to stay inside and finish up a blog post. Once the building is empty and we have all met up in the designated meeting area, we do a roll call and wait for the all-clear to get back to work.
Several years ago the alarms went off. While waiting for the drill to end, we were concerned to see fire fighters arrive and rush into the building. Realizing this was not a drill, there were some tense moments of waiting. The fire chief and our president eventually walked out of the building and our president was yelling for one of our engineers. Turns out the engineer (who shall remain nameless) was cooking a chicken for lunch. Yes, a whole chicken. The chicken didn’t make it – I’m not sure what the guilty engineer had for lunch afterwards. At least we received extra evacuation practice that year. We aren’t allowed to cook whole chickens in the kitchen anymore.
Simpson Strong-Tie is helping increase awareness about earthquake safety and encouraging our customers to participate in the Great ShakeOut, which takes place next Thursday on October 20. It’s the largest earthquake drill in the world. More than 43 million people around the world have already registered on the site.
On October 20, from noon to 2:00 p.m. (PST), earthquake preparedness experts from the Washington Emergency Management Division and FEMA will join scientists with the Washington Department of Natural Resources and the Pacific Northwest Seismic Network for a Reddit Ask Me Anything – an online Q&A. Our very own Emory Montague will be answering questions. The public is invited to ask questions here. (Just remember that this thread opens the day before the event and not sooner.)

We’re also providing resources on how to retrofit homes and buildings, and have information for engineers here and for homeowners here.
Earthquake risk is not just a California issue. According to the USGS, structures in 42 of 50 states are at risk for seismic damage. As many of you know, we have done a considerable amount of earthquake research, and are committed to helping our customers build safer, stronger homes and buildings. We continue to conduct extensive testing at our state-of-the-art Tye Gilb lab in Stockton, California. We have also worked with the City of San Francisco to offer education and retrofit solutions to address their mandatory soft-story building retrofit ordinance and have created a section on our website to give building owners and engineers information to help them meet the requirements of the ordinance.
Last year, Tim Kaucher, our Southwestern regional Engineering Manager, wrote about the City of Los Angeles’s Seismic Safety Plan in this post. Since that time, the City of Los Angeles has put that plan into action by adopting mandatory retrofit ordinances for both soft-story buildings and non-ductile concrete buildings. Fortunately, California has not had a damaging earthquake for some time now. As a structural engineer, I find it encouraging to see government policy makers resist complacency and enact laws to promote public safety.
Participating in the Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drill is a small thing we can all do to make ourselves more prepared for an earthquake. If your office hasn’t signed up for the Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drill, we encourage you to visit shakeout.org and do so now.
California Has Funding for $3,000 Grants for Home Retrofits
Are you an engineer working with California clients whose homes were built before 1979 on a raised foundation?
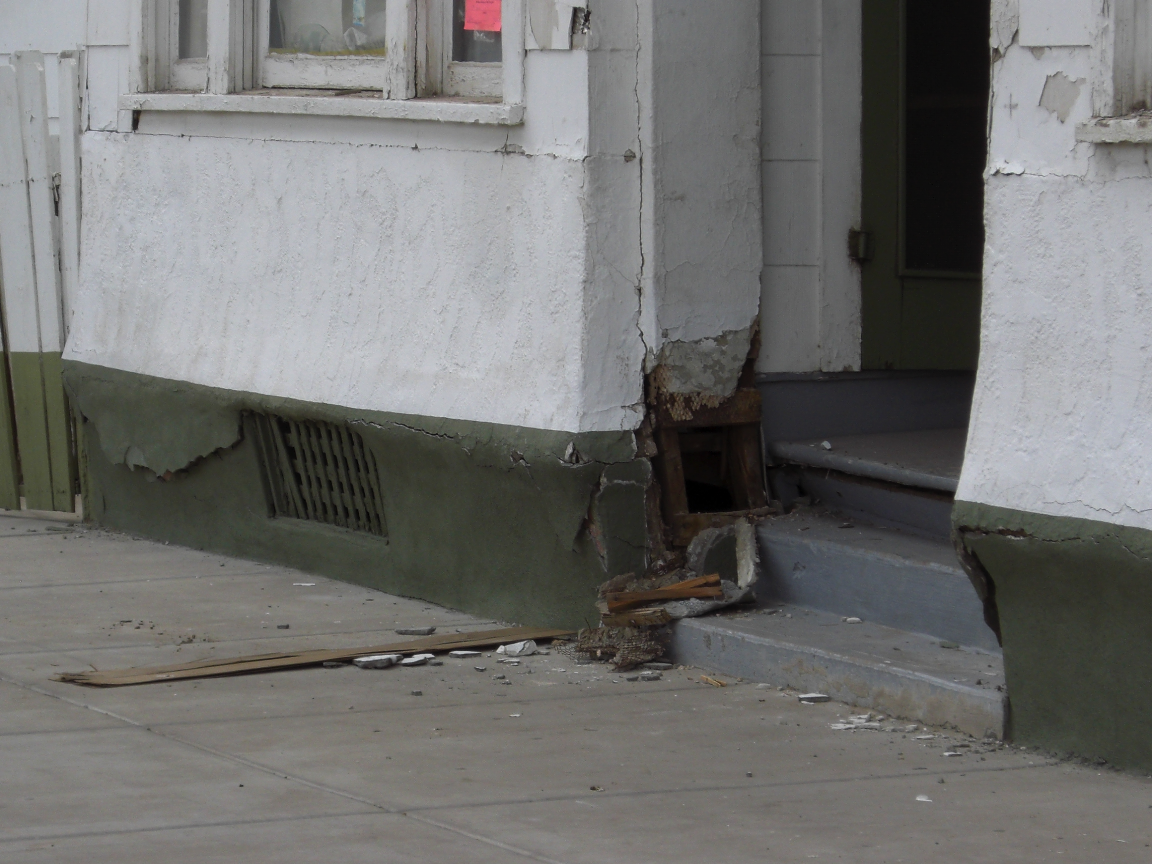

If you are, these clients may be among the 1.2 million California homeowners eligible for a seismic home retrofit. The state of California has approved the continuation of an initiative known as Earthquake Bolt + Brace (EBB). In its second year, this program plans to make as many as 1,600 grants to selected homeowners, nearly three times the number given the previous year. The EBB grant program provides up to $3,000 to homeowners residing in more than 150 California zip codes. Check to see whether your clients live within one of these communities here.
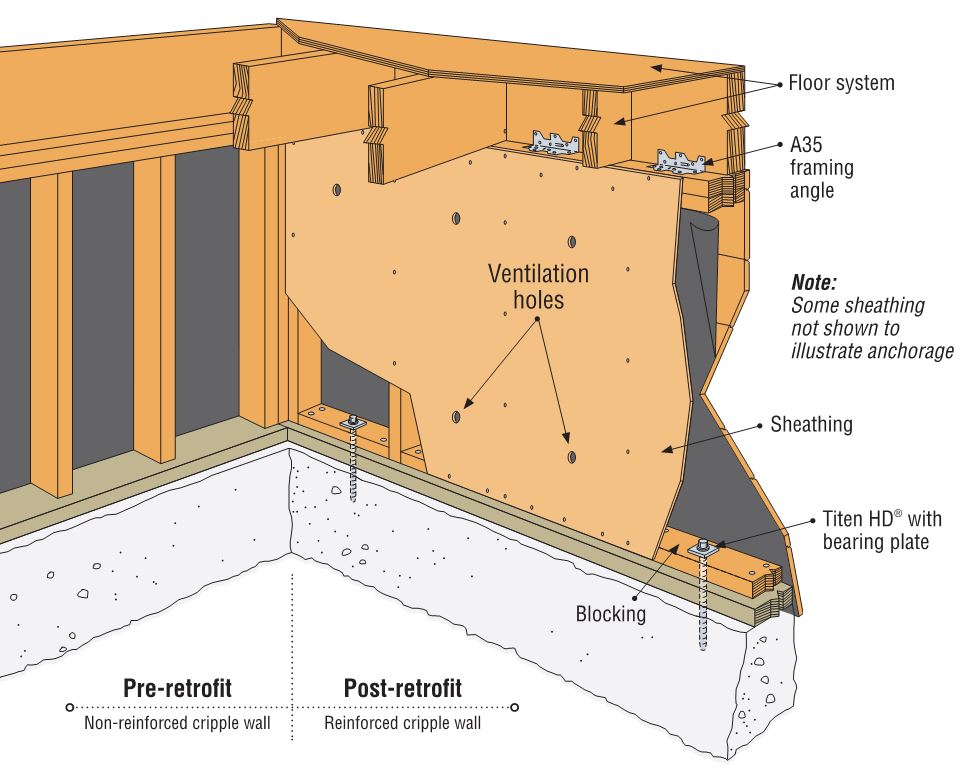
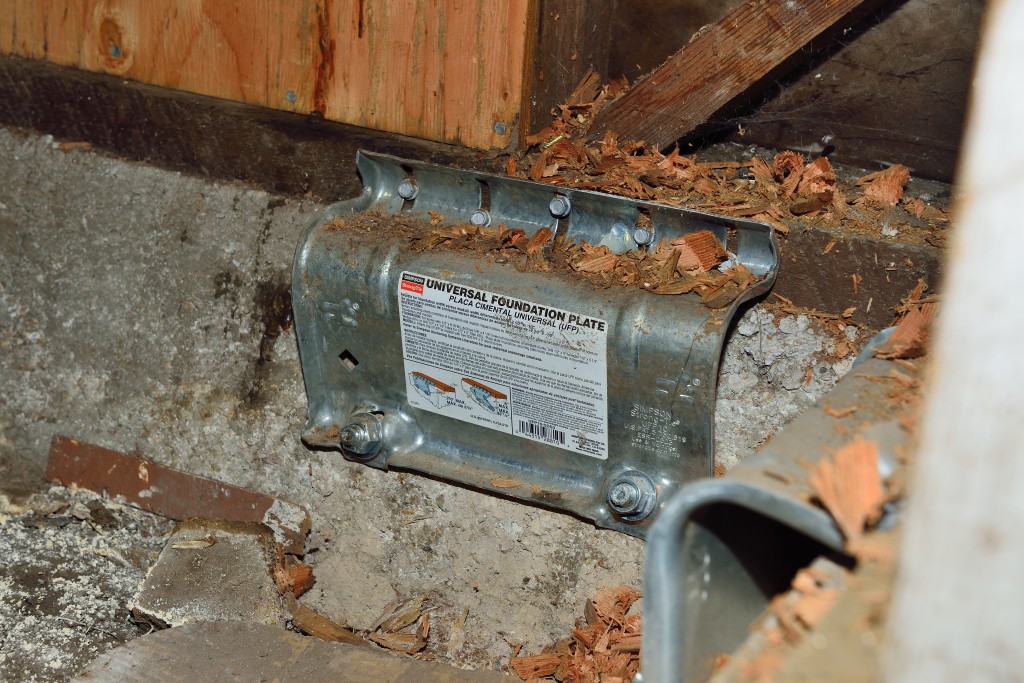
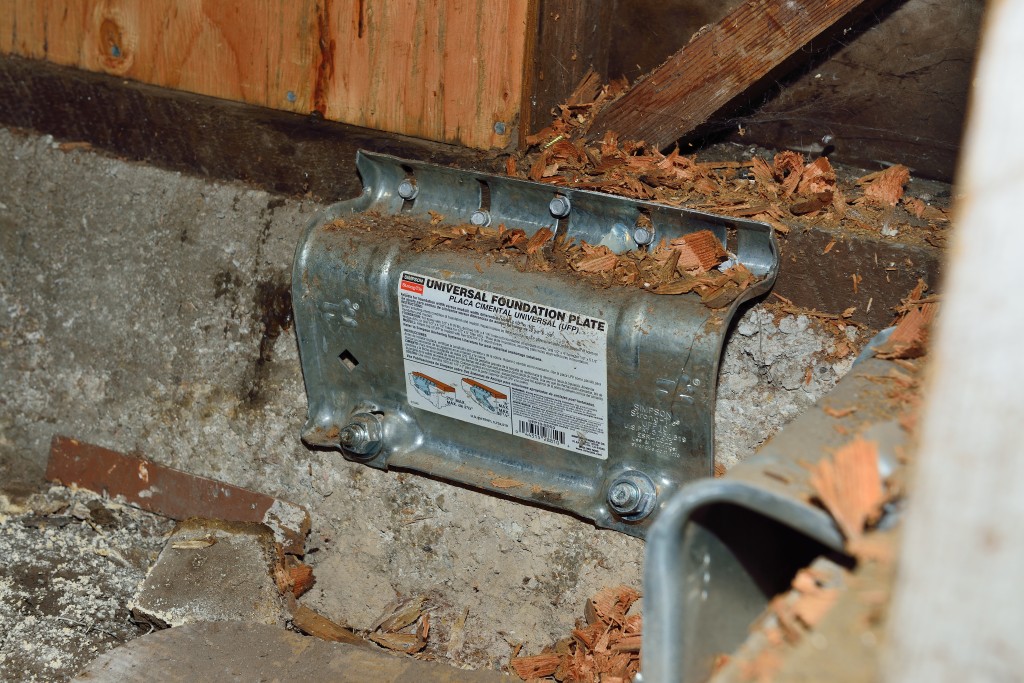
Simpson Strong-Tie has several different resources to assist you in helping your clients understand how to mitigate seismic risks to houses with raised foundations. The Seismic Retrofit Details sheet provides various ways to retrofit the cripple wall system using prescriptive methodologies, which can be adapted for engineered solutions. The picture below highlights the use of the Simpson Strong-Tie universal foundation plate (UFP) to attach the boltless sill plate of the cripple wall to the concrete stemwall. This simple step can help prevent the house from sliding off its foundation. The picture also reveals plywood sheathing used to reinforce the weak cripple wall system. Additional resources for retrofit can be found here.

To help your clients better understand the impact these simple steps can have in preventing structural damage in an earthquake, click here to watch the story of a Napa business women who had purchased a structure with a raised foundation for her business and retrofitted it just prior to the 2014 M6.0 Napa earthquake, which caused considerable damage to many similar structures.
Let your clients know that the time to apply is very limited if they think they qualify for a retrofit grant. Registration for the 2016 EBB program ends on February 20. To register or learn more about the program, visit www.earthquakebracebolt.com.
When you finish a retrofit for one of your clients, we want to hear how it went. Let us know in the comments below.
Resilience by Design: City of Los Angeles Lays Out a Seismic Safety Plan
“From a seismological standpoint, Northridge was not a big earthquake.” This is first sentence of the “Resilience by Design” report by L.A. Mayor’s Seismic Safety Task Force led by Dr. Lucy Jones of the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The report is the culmination of a year-long investigation into the greatest vulnerabilities of the city from a major seismological event. Continue Reading
Seismic Safety Regulations and Solutions
I have a special place in my heart for old buildings. Every college design course I took was related to new design. Concrete, steel, or wood design, the design problem was invariably part of a new building. I thought structural engineers designed new buildings. When I showed up for my first day of work wearing dress pants, a button-down shirt and a tie, I was handed a flashlight, tape measure, a clipboard and a Thomas Guide map (no Google maps back then) and sent to do as-built drawings for a concrete tilt-up that we were retrofitting.
When I was designing buildings, I created a lot of as-built drawings. Figuring out how a building was put together, what the structural system was (or wasn’t!) and designing a lateral load path in these old, and often historic buildings, was immensely satisfying. Knowing that history, it should not be surprising I have done a number of blog posts related to seismic retrofits. Soft-Story Retrofits, San Francisco’s Soft-Story Retrofit Ordinance, Remembering Loma Prieta, Resilient Communities, FEMA P-807, and Home Seismic Retrofit (there are probably a couple I forgot).
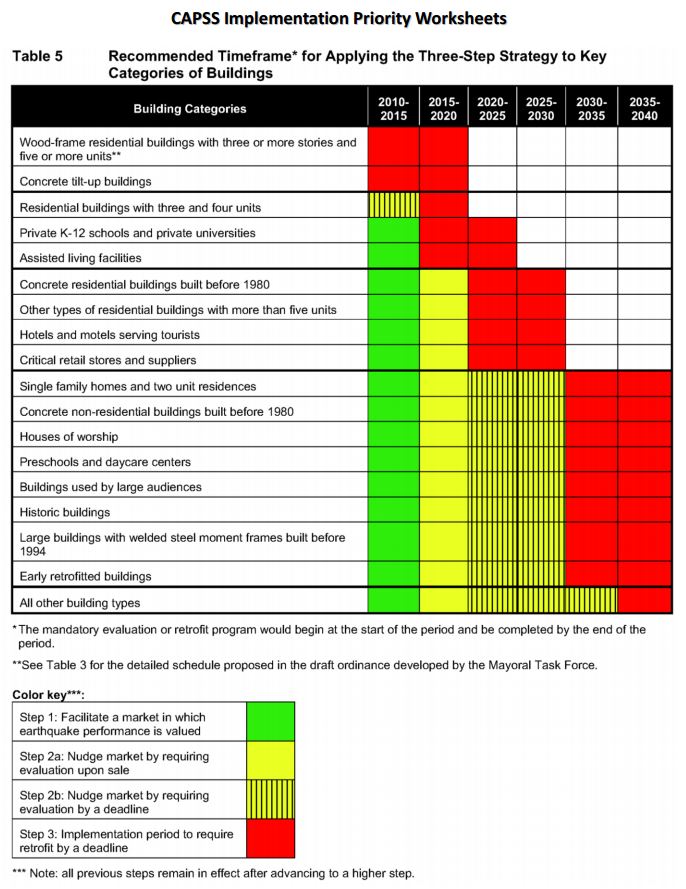
This week, Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti proposed new seismic safety regulations . The recommendations are to retrofit soft-story wood-framed buildings within five years and older concrete buildings within 30 years. While these are only recommendations, it is encouraging to see politicians supporting policies to promote resiliency and life safety.
In San Francisco, thousands of building owners are already required by law to seismically retrofit multi-unit (at least five) soft-story, wood-frame residential structures that have two or more stories over a “soft” or “weak” story. These buildings typically have parking or commercial space on the ground floor with two or more stories above. As a result, the first floor has far more open areas of the wall than it actually has sheathed areas, making it particularly vulnerable to collapse in an earthquake.
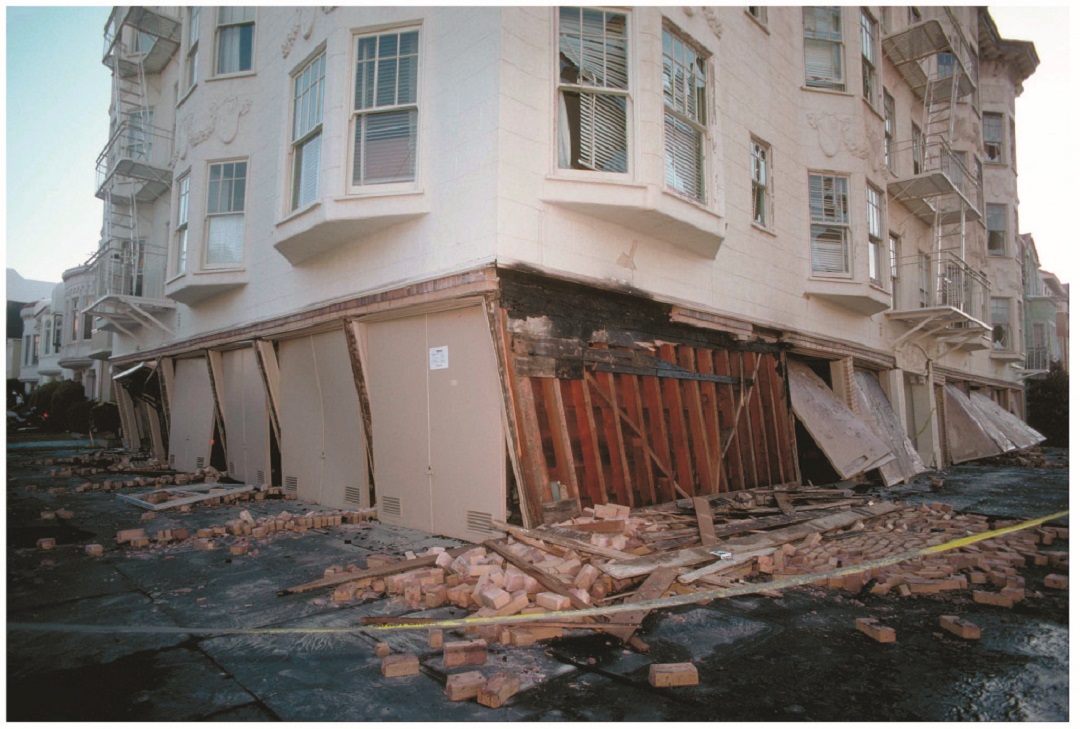

San Francisco’s ordinance affects buildings permitted for construction before Jan. 1, 1978. Mandatory seismic retrofit program notices requiring that buildings be screened were sent out in September, 2013, to more than 6,000 property owners. It is anticipated that approximately 4,000 of those buildings will be required to be retrofitted by 2020.
“When we look at the demographic of these buildings, they house approximately 110,000 San Franciscans. It’s paramount that we have housing for people after a disaster. We know we will see issues in all types of buildings, but this is an opportunity for us to be able to retrofit these buildings while keeping an estimated 1100,000 San Franciscans in their homes and, by the way of retrofit, allowing them to shelter in place after a disaster,” according to Patrick Otellini, San Francisco’s chief resilience officer and director of the city’s Earthquake Safety Implementation Program. “This exponentially kick starts the city’s recovery process.”
One solution to strengthen such buildings is the Simpson Strong-Tie® Strong Frame® special moment frame. Its patented Yield-Link™ structural fuses are designed to bear the brunt of lateral forces during an earthquake, isolating damage within the frame and keeping the structural integrity of the beams and columns intact.
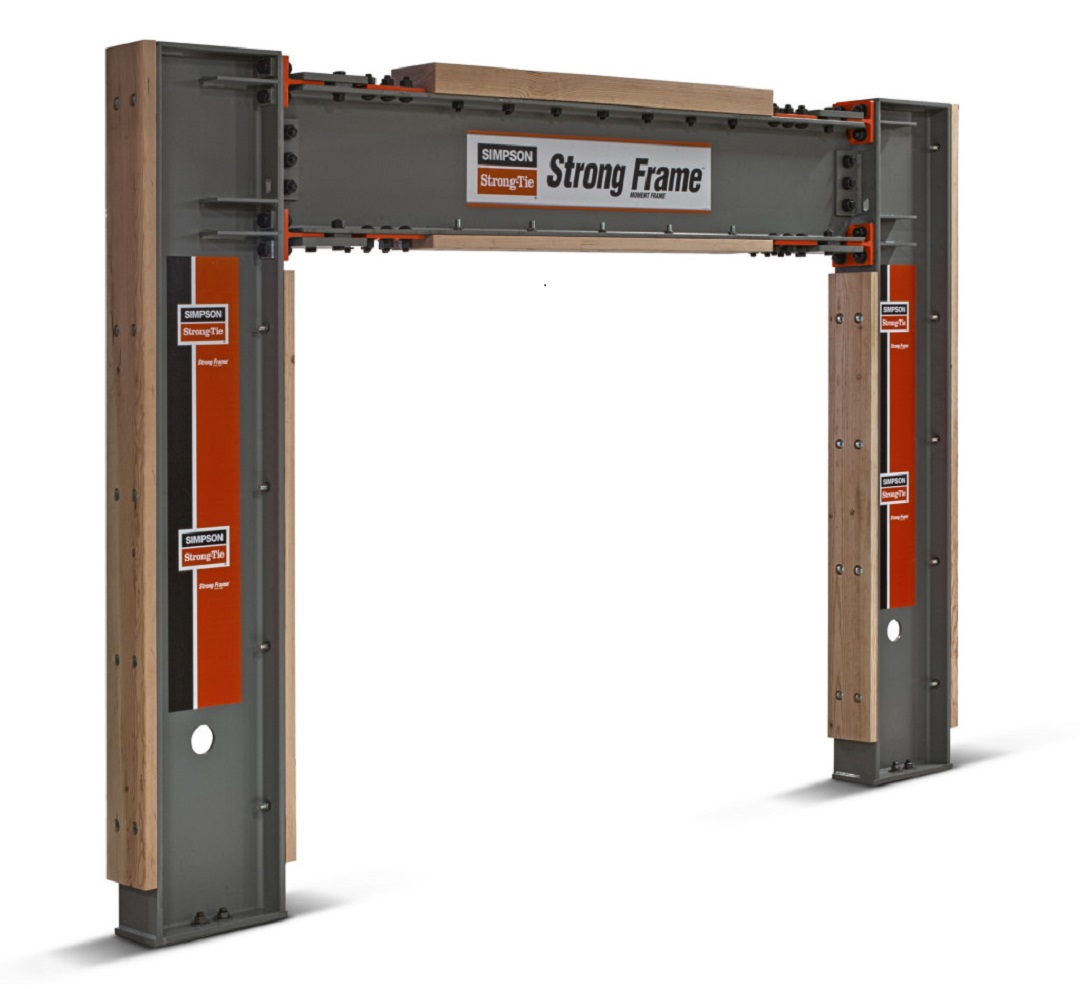

“The structural fuses connect the beams to the columns. These fuses are designed to stretch and yield when the beam twists against the column, rather than the beam itself, and because of this the beams can be designed without bracing. This allows the Strong Frame to become a part of the wood building and perform in the way it’s supposed to,” said Steve Pryor, S.E., International Director of Building Systems at Simpson Strong-Tie. “It’s also the only commercially-available frame that bolts together and has the type of ductile capacity that can work inside of a wood-frame building.”
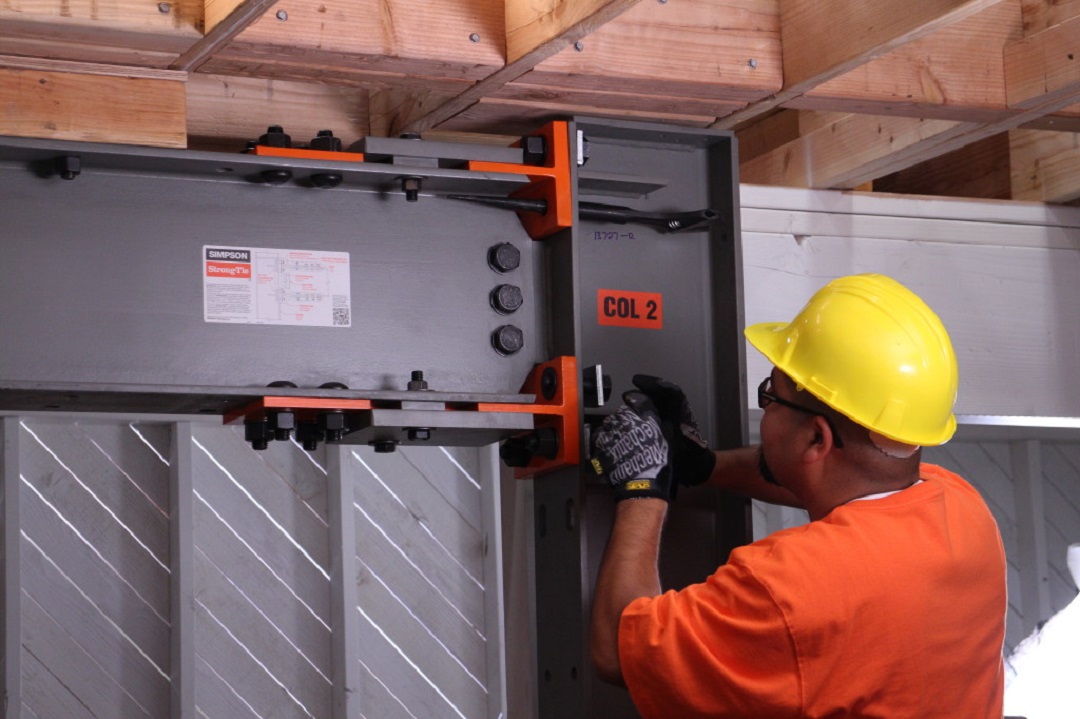

Another key advantage of the Simpson Strong-Tie special moment frame is no field welding is required, which eliminates the risk of fire in San Francisco’s older wood-framed buildings.
To learn more about San Francisco’s retrofit ordinance, watch a new video posted on strongtie.com/softstory. For more information about the Strong Frame special moment frame, visit strongtie.com/strongframe.
Remembering Loma Prieta
We all know that earthquakes physically shape the landscape here in California, but they shape careers as well. Earthquakes I felt while growing up in California’s southern San Joaquin Valley got me thinking about engineering as a career while in high school. When the Loma Prieta earthquake struck on October 17, 1989, like many of you I was watching the World Series live on television and thus got to see the earthquake live as well. I was in my senior year of college at the time, studying Civil Engineering with a structural emphasis. This earthquake cemented the direction I would take in my career. I wanted to be a structural engineer, and I wanted to design buildings that would not fall down in earthquakes.
Applying new FEMA P-807 Weak Story Tool to Soft-Story Retrofit
We have written about San Francisco’s Soft-Story Retrofit Ordinance and Soft-Story Retrofits before on the blog. I wanted to discuss in more detail the issues with soft story buildings and FEMA’s new tool for addressing them. Under the San Francisco Ordinance, wood-framed residential structures that have two or more stories over a “soft” or “weak” story require seismic retrofit. So far, more than 6,000 property owners have been notified about complying with the mandate.Continue Reading
Home Seismic Retrofit
The 6.0 magnitude earthquake that struck Napa, CA, in August caused more than 200 injuries and structural damage to many homes and businesses throughout the area. The quake was the largest to hit the San Francisco Bay Area since the Loma Prieta earthquake (6.9 magnitude) in 1989, prompting the governor to declare a state of emergency.
I have done several posts about San Francisco’s Soft-Story Retrofit Ordinance and some of NEES-Soft testing related to soft-story retrofits. The soft-story ordinance only addresses multi-unit residential units and does not require retrofit of single-family homes. Cities are reluctant to mandate seismic evaluation and retrofit of single-family homes for a number of reasons that I won’t discuss here. The draft Earthquake Safety Implementation Program (ESIP) for San Francisco will not recommend mandatory retrofit of single-family homes until 2030.
The good news is homeowners can retrofit their homes without waiting for the government. A couple years ago in this post, I discussed some of the tools available to retrofit existing buildings.
One of these tools is the 2012 International Existing Building Code (IEBC). The IEBC has provisions for repair, alteration, addition or change of occupancy in existing buildings and for strengthening existing buildings. For alterations, these provisions may not comply with current IBC requirements, but they are intended to maintain basic levels of fire and structural life safety. The IEBC also provides prescriptive provisions for strengthening existing buildings against earthquake damage, which include strengthening residential houses on raised or cripple wall foundations.
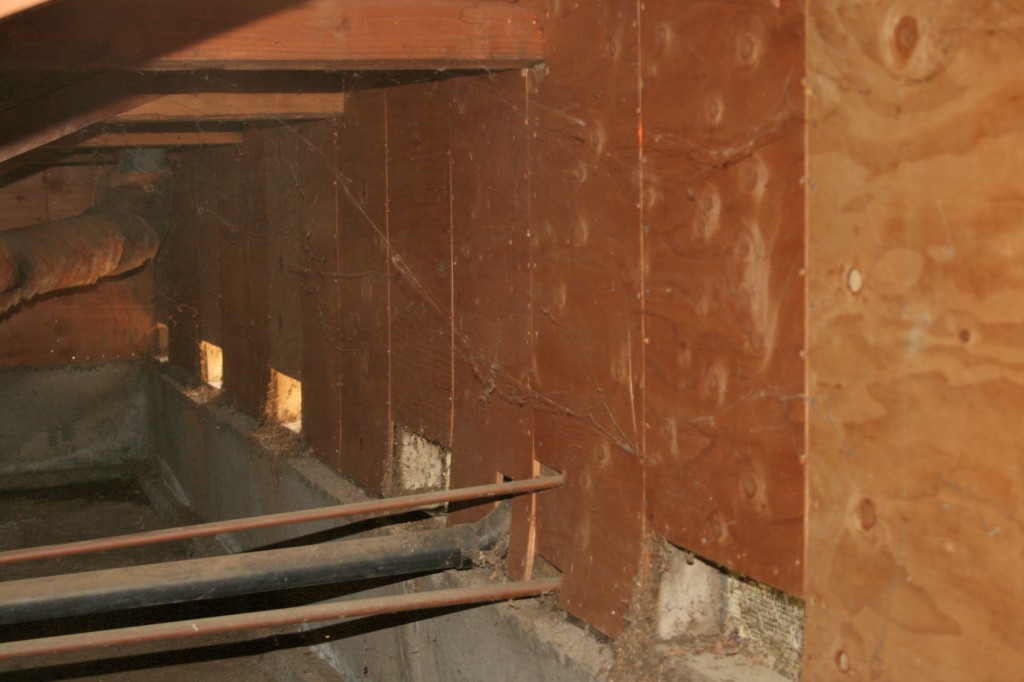

Cripple wall failures are a common type of damage observed in older homes, caused by inadequate shear strength in the cripple wall. An additional failure point is the attachment of the wood sill plate to the foundation. Having a strong connection between the wood structure and the concrete foundation is critical in an earthquake. Since the work required to strengthen these connections is typically performed in a crawlspace or unfinished basement, it is a relatively low-cost upgrade that is extremely beneficial to structural performance.

Our website has information for retrofitting your home. The Seismic Retrofit Guide has information about how earthquakes affect a home and the steps to take to reinforce the structural frame of a house. The Seismic Retrofit Detail Sheet is intended to help building departments, contractors and homeowners with seismic retrofitting. It includes common retrofit solutions for reinforcing cripple walls and foundation connections.
One business owner in Napa chose to retrofit her building when she purchased it. You can see her video narrative here.