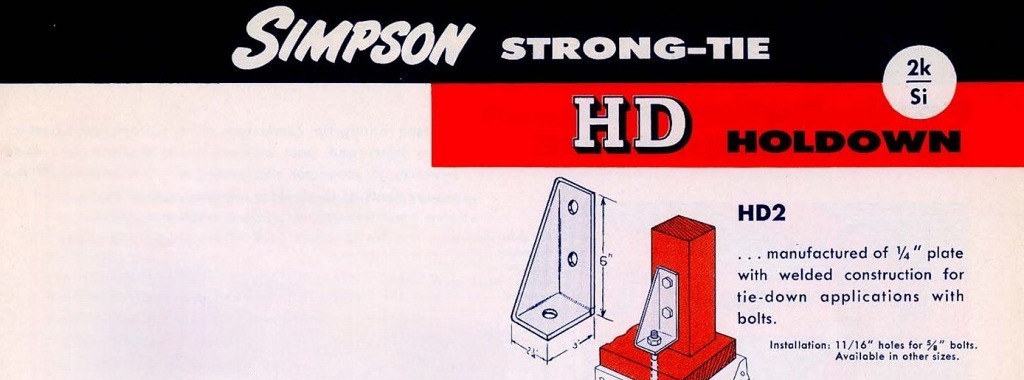
Holdowns first appeared in the 1966 connector catalog — all two of them. The HD24 was an embedded strap that used either nails or bolts, and the HD2 used bolts to the post and an anchor bolt to the concrete. This first sighting of holdowns was missing a list of allowable loads.
Tag: nails
Second Day of Trivia – Hurricane Ties
I recently wrote about the H1A hurricane tie in this post, which discussed the original H1 hurricane tie first appearing in 1972, and the subsequent changes over the years that led to our current H1A. The original H1 along with the H2 and the H3 were the first products to appear under the label “hurricane ties” in our catalog.
Revisiting Stainless-Steel Nail Calculations . . . .
Those of you who have been following the Simpson Strong-Tie SE Blog for a while may recall our 2013 blog post on the withdrawal resistance of stainless-steel nails. There have been several developments relating to that subject since that blog was posted, and we want to help you catch up.Continue Reading
How to Pick a Connector Series – Selecting Fasteners
The parts won’t hold themselves up. They have to be fastened in place.
The previous blog in the How to Pick a Connector Series by Randy Shackelford, on “ Selecting a Joist Hanger,” covered the available Simpson Strong-Tie joist hanger options and how to pick a hanger for your design. This week’s blog focuses on the fasteners recommended for various wood connectors.
For straps, holdowns and other connectors, the first step is to specify a product that meets the load and corrosion resistance requirements. Then, specify fastening that is appropriate. The Wood Construction Connectors catalog, C-C-2015, offers fastener information for every Simpson Strong-Tie connector used in wood construction. If you specify the type and number of fasteners and install them as shown in the catalog, then your installation will get full design values. Many connectors are designed to be installed with either nails or Strong-Drive® SD Connector screws. Some products must be installed with Strong-Drive SDS Heavy-Duty Connector screws. Figure 1 is a snip from page 76 of catalog C-C-2015. Here the face-mount hanger table gives the size and number of nails to be installed in the header and the joist, and the table note defines the nail size terminology. Let’s take a look at the various fasteners used for Simpson Strong-Tie connectors of all varieties.
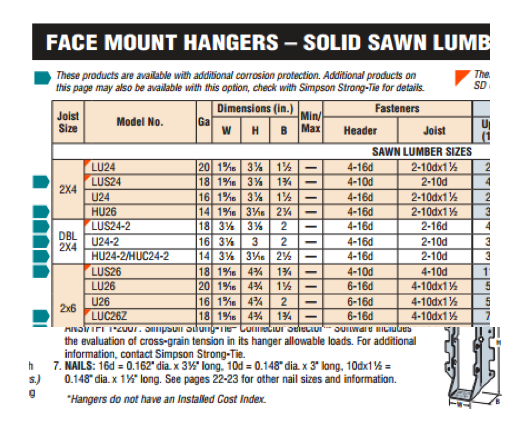
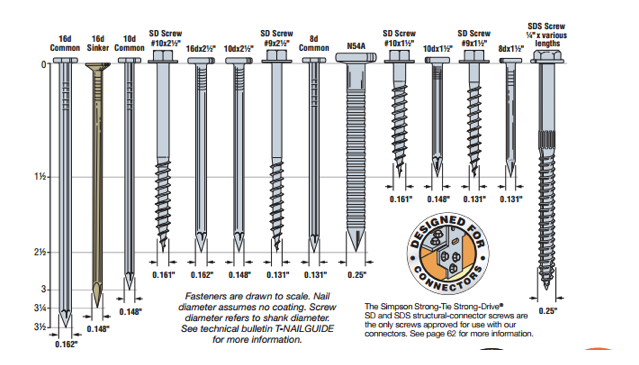
Figure 2 shows a scale view of almost all of the fasteners used with connectors. You can find this illustration in the Fastening Systems catalog, C-F-14, and the Wood Construction Connectors catalog, C-C-2015. However, we are continually designing, evaluating and adding new fasteners to use with our connectors. Check our website for the latest and greatest.
Keep in mind some generalities that are to be considered in every connector fastener specification.
- Type and size – Be sure to specify the correct type of fastener and size; for nails, that means diameter and length.
- Do not mix fasteners – Do not combine nails and screws in the same connector unless specifically allowed to do so in the load table.
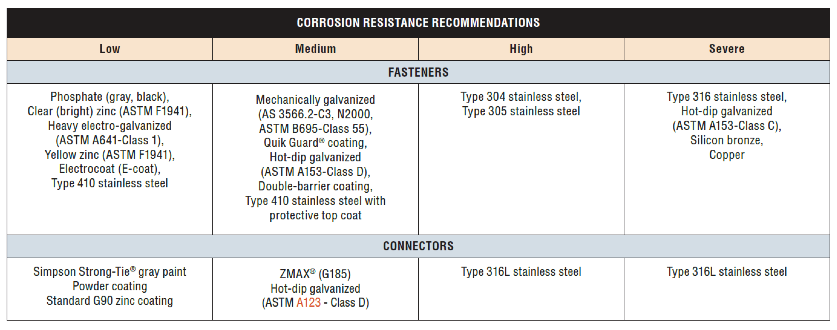
- Corrosion resistance – Consider environmental corrosion and galvanic corrosion. For environmental corrosion, specify fasteners that have corrosion resistance similar to the connector; for galvanic corrosion, the fasteners and connector should be galvanically compatible. Figure 3 shows the corrosion resistance recommendations for fasteners and connectors.
NAILS
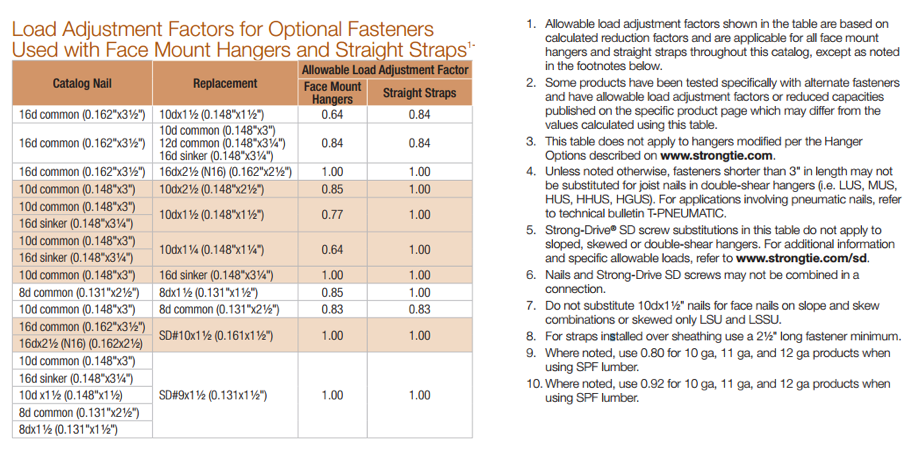
Nail terminology is messy. In a recent Structure Magazine article (July 2016), the author made the point that nail specifications are frequently misinterpreted (or overlooked), and as a result the built system does not have the intended design capacity. In general construction vernacular, specification by penny size identifies only the length. For example, a “10d” specification could be interpreted to mean 10d common – 0.148″ x 3″, 10d box – 0.128″ x 3″, 10d sinker – 0.120″ x 2.875″, or the 10d x 2.5″ – 0.148″ x 2.5″. See NDS-12, Appendix L, Table L4 for the length, nail diameter and head diameter of Common, Box, and Sinker steel wire nails. What if the face-mount hanger needed 0.148”x3” nails to achieve full load, but the face-mount hanger was installed with 0.148″ x2.5″? In this case, the nail substitution causes a reduction in load capacity of 15%. The load capacity losses would be even greater if 10d sinker or 10d box nails were used. The load adjustment factors for nail substitutions used with face- mount hangers and straight straps are shown in Table 3.
Simpson Strong-Tie nail terminology further complicates nail specification because, in Strong-Tie lingo, the penny reference is to diameter (not to length). This is further reason to write nail specifications in terms of diameter and length.
The best way to prevent mistakes is to specify nails by both length AND diameter.
There are two types of connector nails available, the Strong-Drive® SCNR Ring-Shank Connector nail and the Strong-Drive SCN Smooth-Shank Connector nail. SCN stands for Structural Connector Nails. R would refer to ring- shank nails. Currently most ring-shank connector nails are available in Type 316 stainless steel. Reasons for this are discussed here. The smooth-shank nails are made of carbon steel and either have a hot-dip galvanized (HDG) finish meeting the specifications of ASTM A153, Class D, or have a bright finish. Stainless-steel ring-shank nails are recommended for stainless-steel connectors. Use hot-dip galvanized nails with ZMAX® and HDG connectors. See Table 1 for the nail properties.
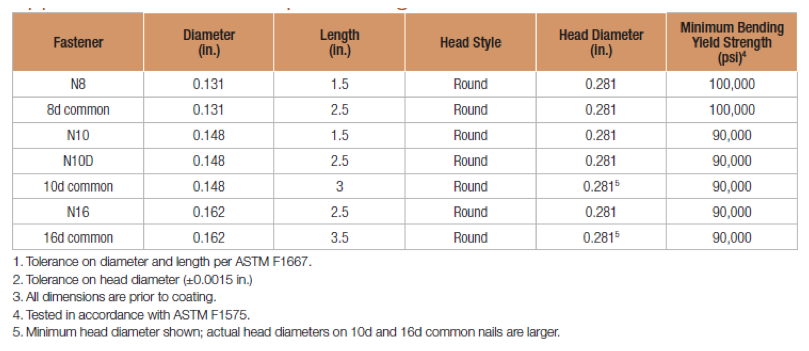
Simpson Strong-Tie connector nail specifications include common nails, sinker nails and short nails. Nails used in connectors should always have a full round head and meet the bending yield requirements of ASTM F1667, Table S1. Nails can be driven with a hammer or power-driven. Table 2 shows the Strong-Tie connector nails by catalog name, size and model number.
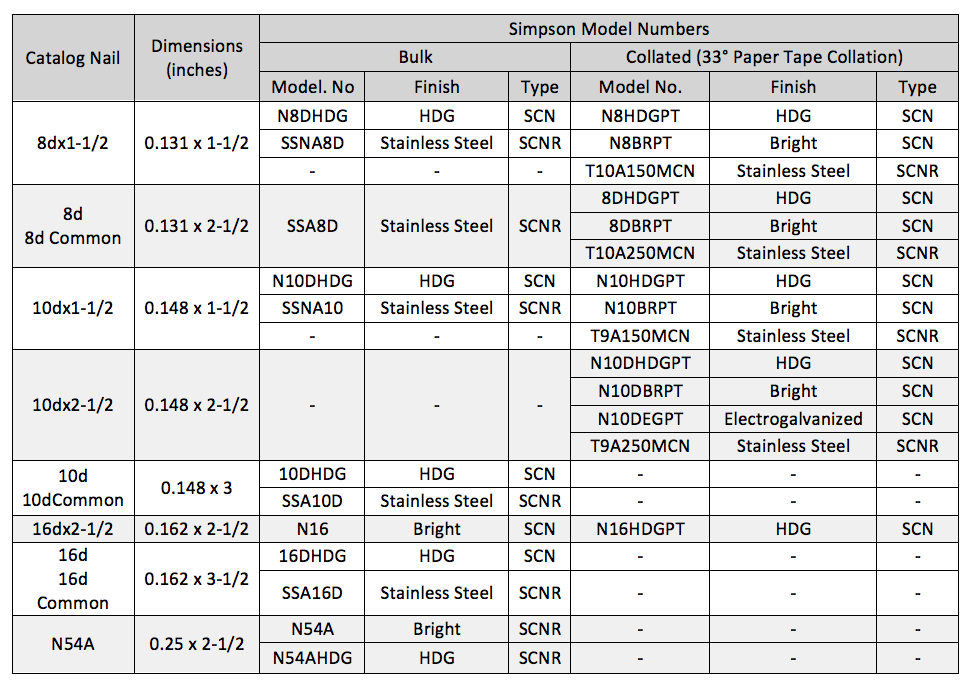
Remember that connector double-shear nailing should always use full-length common nails. Do not use shorter nails in double-shear conditions.
Table 3 is snipped from the Fastening Systems catalog, and it shows load adjustment factors for optional fasteners used in face-mount hangers and straps.
SD Screws

Almost 150 Simpson Strong-Tie connectors can be installed with Simpson Strong-Tie Strong-Drive® SD Connector screws (Figure 4). The shanks of the SD Connector screws are designed to match the fastener holes in Simpson Strong-tie connectors. The screw features, dimensions, strengths and allowable single-fastener properties are given in ICC-ES ESR-3046, and the SD screws have been qualified for use in engineered wood products. See ICC-ES ESR-3096 for code-approved connectors installed with SD screws.
SD screws can make connector and strap installation easier and can also provide some resistance that is needed beyond what might be offered by nails. Ease of installation is sometimes an issue in tight places where it might be much easier to use a screw-driving tool rather than a hammer or a power nailer. Some installations are improved by using screws instead of nails, especially where pulling away from the mounting member is a possible failure mode. For example, joist hangers for a deck need withdrawal resistance to help keep the deck tightly connected to the ledger.
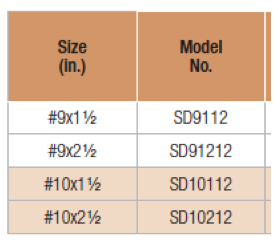
SD screws are available in four sizes as shown in Table 4 below. These screws are mechanically galvanized per ASTM B695, Class 55, and have corrosion-resistance qualifications for use in chemically treated wood for Exposure Conditions 1 and 3 per ICC-ES AC257, which is the acceptance criterion for Corrosion-Resistant Fasteners and Evaluation of Corrosion Effects of Wood Treatment Chemicals. See ICC-ES ESR-3046 for corrosion resistance details. Visit SD Screws in Connectors for a complete list of connectors that can be installed with SD screws.
Here are a few specification and construction tips for SD screws:
- SD10 screws replace 16d common and N16 nails in face-mount hangers and straps.
- SD9 screws replace 8d and 10d common and 1-1/2″ size nails and 16d sinker nails (all nails 0.148″ and 0.131″ diameter) in face-mount hangers and straps.
- When SD screws are to be an alternative to nails, specify and use only SD screws. Other types of screws shall not be substituted.
- SD screws are required to be installed by turning. Do not drive them with a hammer or palm nailer!
- SD screws and nails cannot be mixed in the same connector.
SDS Screws

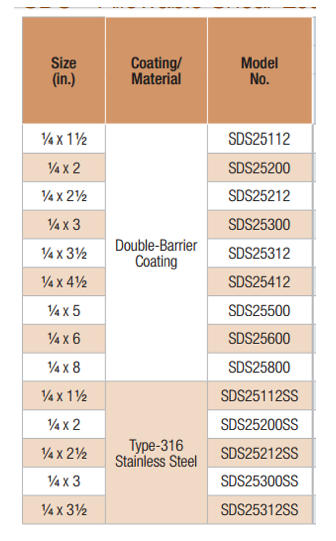
The Simpson Strong-Tie Strong Drive® SDS Heavy-Duty Connector screws are 1/4″ screws with a hex washer head (Figure 5). They are available in nine lengths. Table 5 shows the available SDS screws. SDS Screws are available with a double-barrier coating or in Type 316 stainless steel. These screws can be installed with no predrilling and have been extensively tested in various applications. SDS screws can be used for both interior and exterior applications. See ICC-ES ESR-2236 for dimensions, mechanical properties and single-fastener allowable properties. As shown in the evaluation report, SDS screws are also qualified for use in chemically treated wood. See the evaluation report for particulars. SDS screws also have been qualified for use in engineered wood products.
If you need more information about the nails and screws recommended for use with Simpson Strong-Tie connectors, visit strongtie.com and see the appropriate catalog, flier or engineering letter. Remember, your choice of fasteners affects the load capacity of your connections.
Let us know if you have any comments on Simpson Strong-Tie fasteners for straps, holdowns and other connectors.